VPN technologies have long been the backbone of remote access, but according to new ThreatLabz research, the security risks and performance challenges of VPNs may be rapidly changing the status quo for enterprises.
The Zscaler ThreatLabz 2025 VPN Risk Report with Cybersecurity Insiders draws on the insights of more than 600 IT and security professionals on the growing risks and operational challenges posed by VPNs. It reveals that enterprises are actively grappling with the security risks, performance challenges, and operational complexity of VPNs. One key striking trend: enterprises are beginning to transition en masse to adopt zero trust solutions. Overall, 65% of organizations plan to replace VPN services within the year, a 23% jump from last year’s findings. Meanwhile, 96% of organizations favor a zero trust approach, and 81% plan to implement zero trust strategies within the next 12 months.
All of these shifts, meanwhile, happen within the context of an AI-enabled threat landscape. Because VPNs are internet-connected, it has become relatively straightforward for attackers to use AI for automated recon targeting VPN vulnerabilities. This can take the form of simply asking your favorite AI chatbot to return all current CVEs for VPN products in use by an enterprise, which are then easily scanned over the public internet. When you consider that researchers have recently discovered that tens of thousands of public IP addresses hosted by at least one of the largest security providers are being actively scanned, likely by attackers, the crux of the problem for VPNs becomes clear: if you’re reachable, you’re reachable.
The report analyzes these risks in the context of enterprise concerns, plans, and their adoption of zero trust strategies to secure the hybrid workforce and enable secure connectivity to private applications. Below, this blog post discusses three key findings from the report underlying these critical shifts. For full insights, analysis, and best practices, download the Zscaler ThreatLabz 2025 VPN Risk Report today.
1. The widespread security challenges of VPNs
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) were once the gold standard for enabling secure remote access. But as cyber threats evolve, VPNs have shifted from trusted tools to major liabilities. Indeed, VPN vulnerabilities are proving irresistible for attackers; 56% of organizations reported VPN-exploited breaches reported last year, a notable rise from the year prior.
Such vulnerabilities pose a central challenge. Because VPNs are internet-connected devices, threat actors can easily probe for impacted VPN infrastructure and exploit it before any patch is released or has been applied. Recently, CISA issued an advisory for impacted organizations to apply security updates for CVE-2025-22457, now a known-exploited critical vulnerability that may allow unauthenticated attackers to achieve remote code execution (RCE).
These gaps have become prime entry points for ransomware campaigns, credential theft, and cyber espionage campaigns that can cause widespread damage across networks. Indeed, a staggering 92% of respondents share concerns that unpatched VPN flaws directly lead to ransomware incidents—highlighting how difficult it is to continuously patch VPNs in time. Meanwhile, 93% of respondents express concerns over backdoor vulnerabilities introduced by third-party VPN connections, as attackers increasingly exploit third-party credentials to breach networks undetected.
Mapping the rise of VPN CVEs from 2020-2025
In an effort to understand the rise of VPN vulnerabilities, ThreatLabz also analyzed VPN Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVEs) from 2020 to 2025 based on data from the MITRE CVE Program. In general, vulnerability reporting is a good thing, as rapid vulnerability disclosure and patching helps the entire ecosystem improve cyber hygiene, improve community collaboration, and quickly respond to new vectors of attack. No type of software is immune from vulnerabilities, nor should it be expected to be.
Zscaler
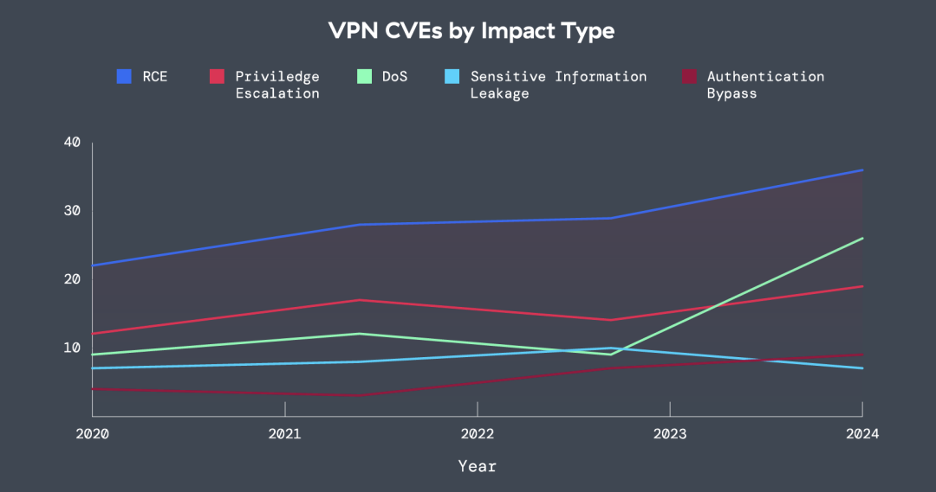
Figure 1: The impact type of VPN CVEs from 2020-2024, covering remote code execution (RCE), privilege escalation, DoS, sensitive information leakage, and authentication bypass.
How these CVEs are discovered and the information they contain reflect changes in the evolving threat landscape. In the case of VPNs, ThreatLabz found that not only have VPN vulnerabilities increased over time — in part reflecting their popularity during the post-COVID transition to hybrid work — but they are often severe.
Over the sample period, VPN CVEs grew by 82.5% (note that early 2025 data has been removed for this portion of the analysis). In the past year, roughly 60% of the vulnerabilities indicated a high or critical CVSS score — indicating a potentially serious risk to impacted organizations. Moreover, ThreatLabz found that vulnerabilities enabling remote code execution (RCE) were the most prevalent kind in terms of the impact or capabilities they can grant to attackers. These types of vulnerabilities are typically serious, as they can grant attackers the ability to execute arbitrary code on the system. Put another way, far from being innocuous, the bulk of VPN CVEs are leaving their customers vulnerable to exploits that attackers can, and often do, exploit.
As enterprises race to keep pace with advancing attacker sophistication, organizations are turning to other options. Zero trust architectures are emerging as the solution for filling these security gaps. Unlike VPNs, which rely on implicit trust and broad network access, zero trust frameworks enforce granular, identity-driven access policies that directly mitigate attacker movement within networks — and remove the risk of internet- and network-connected assets that can be easily scanned for and exploited by attackers.
2. End-user frustration driving enterprise decision-making
VPN inefficiencies aren’t just a problem for security—they’re frustrating users. Slow connectivity, frequent disconnections, and complex authentication processes have plagued VPN users for years — and these challenges top the list of end-user frustrations in our findings. According to the report, these user experience frustrations are increasingly influencing IT strategies, with enterprises looking to zero trust to deliver secure access without performance challenges or compromises.
Zero trust models achieve this by bypassing centralized network dependencies in favor of direct, application-specific connections. The result? Employees gain swift and seamless access to the tools they need, while IT teams can ensure security posture checks and policy enforcement in real-time. Unsurprisingly, satisfaction with zero trust solutions spans both end users and IT teams, solidifying this approach as the next evolution of secure access.
3. 81% of organizations are actively transitioning to Zero Trust frameworks
As a result of these trends, a widespread realization is transforming cybersecurity strategies: zero trust isn’t just conceptual anymore—it’s fundamental. With 81% of organizations actively implementing zero trust frameworks within the next year, enterprises are pivoting away from legacy VPN systems that fail to meet the remote access demands of businesses today. This shift marks a key transition from viewing zero trust as a theoretical ideal to adopting it as a practical solution.
What makes zero trust the favored approach? Unlike VPNs, which typically grant broad network access based on implicit trust, zero trust operates on the principle of “never trust, always verify.” Zero trust enables highly granular access controls to private applications, robust identity verification, and continuous monitoring, delivering effective protection for distributed workforces and hybrid IT environments. In general, enterprises that have transitioned to zero trust from a VPN technology found improved security and compliance as the primary advantage (76%) — reinforcing how zero trust replaces implicit network access and reduces exposure to ransomware, credential theft, and lateral movement risks. Coupled with gains in scalability, compliance, and operational simplicity, it’s increasingly clear why zero trust architectures are rapidly replacing VPNs.
Get the report
For enterprises seeking perspective on VPN and remote access, the ThreatLabz 2025 VPN Risk Report provides key insights. Download your copy for critical insights into:
- Enterprise security and operational challenges of VPN
- Critical best practice for securing the hybrid workforce
- Peer insights into the zero trust transition
- VPN predictions for 2025 and beyond
Read More from This Article: Why 81% of organizations plan to adopt zero trust by 2026
Source: News


