Get in touch with one of our experts
Pandemic is defined by the dictionary as “(of a disease) prevalent throughout an entire country, continent, or the whole world; epidemic over a large area.”
Much of 2020 saw one of the worst global pandemics we have faced. The medical situation this raises with respect to testing, validating, and tracking patient health has placed a heavy load on medical practitioners and patients.
In a global pandemic such as this, it can be hard for medical practitioners and patients to get connected and treated. Continually being on top of patients’ progress is also a challenge, along with scarcity of doctors who themselves are affected by the pandemic.
In this post, we will share an architectural reference from Capgemini for an Amazon Web Services (AWS) native solution that can help solve these problems for patients and doctors.
The solution architecture uses AWS machine learning (ML) services to enable doctors and patients to interact with the least amount of physical contact, while also improving efficiency in treatment management, tracking, and auditing.
Furthermore, the solution provides the base capabilities required in predicting the susceptibility on an infection in a particular region when integrated with other systems in a region/state.
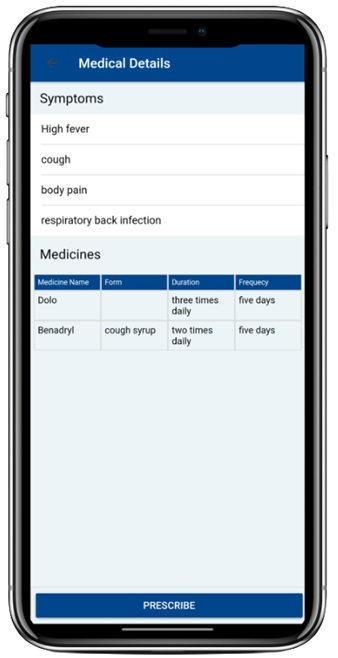
Patients can book an appointment via the Patient’s Voice Bot, and doctors can view the patient’s information and appointment details via the Doctor’s Voice Bot. Doctors can prescribe medicine via voice, and they can also view patient history, diagnoses provided, and appointments (past and future).
Capgemini is an AWS Premier Consulting Partner and Managed Service Provider (MSP). With a multicultural team of 220,000 people in 40+ countries, Capgemini has more than 6,000 people trained on AWS and 1,500 AWS Certified professionals.
Architecture
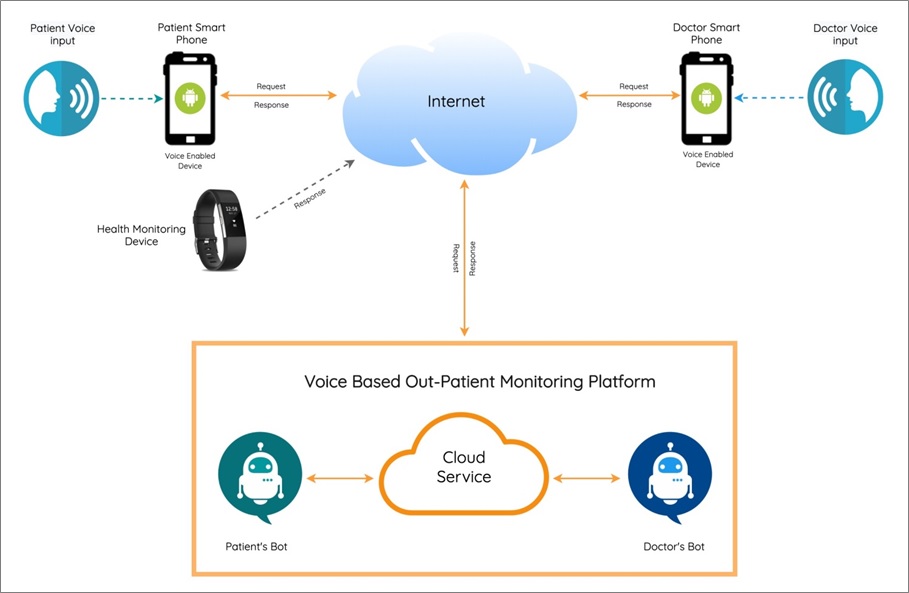
Capgemini’s solution provides an interface for the patient and another separate interface for the doctors, enabling better security control over who gets access to what data set.
The solution encompasses the following:
- Voice input/feedback-based provision (via smartphones) for patients.
- Central patient and diagnosis management system on AWS.
- Voice input/feedback-based provision for doctors and health practitioners.
The solution uses a voice-based recording and monitoring platform as the core. This provides capabilities for a chat-based interface/bot at the patient and doctor end. The interface asks and listens to questions, enters and maintains responses to the backend, and pushes notifications to medical practitioners that appear on a desktop, laptop, or phone.
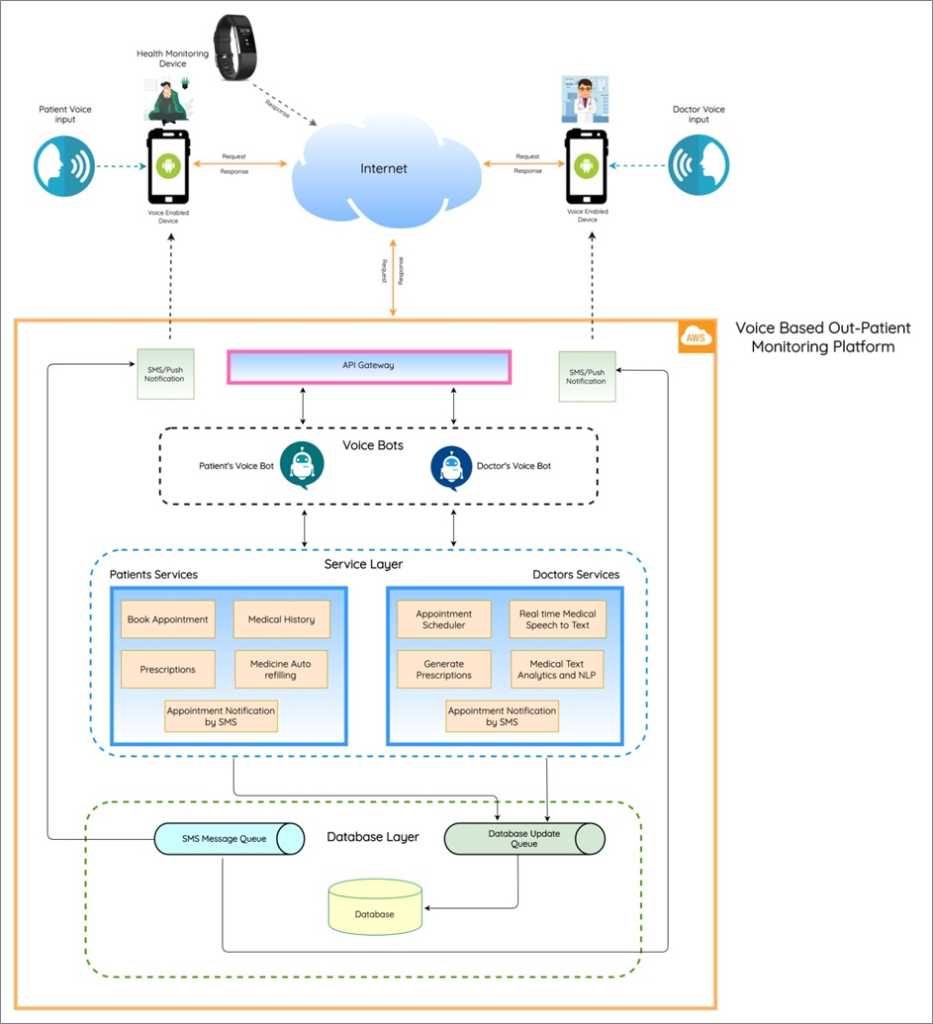
The following diagram represents an expanded view of the voice platform. This exposes its services to the two frontends (doctor and patient access apps) via API gateways. The gateway hosts authentication and data retrieval services, and integration to voice, service, and data layers as shown below.
The next diagram is a view of different services used to materialize the solution blueprint. Further integration is also possible with patient monitoring solutions that can be integrated into the service layer.
The diagram shows one such possibility where a Raspberry Pi-based patient monitoring systems can integrate to the service layer to enrich patient information for doctors to review.
Building the solution
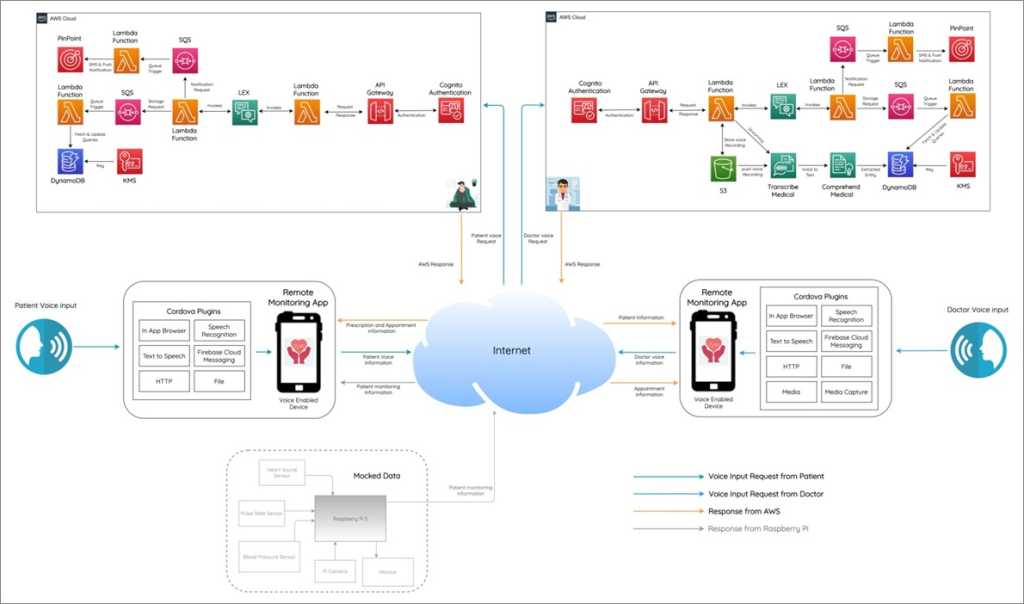
Capgemini developed the solution using Hybrid Mobile Application (Ionic Angular Framework) on AWS. This framework allows developers to write code for a mobile app once and still accommodate to multiple platforms (iOS, Android, Web, and PWA).
The end user (doctors and patients, in this case) will use a mobile application interface as part of the solution. Amazon Cognito services are used as part of authentication with OAuth 2.0-enabled user pools, created separately for doctors and patients.
A user pool is a user directory in Amazon Cognito where users can sign in to your web or mobile app. They can also sign in through social identity providers like Google, Facebook, Amazon, or Apple, and through SAML identity providers. Whether users sign in directly or through a third party, all members of the user pool have a directory profile you can access through a Software Development Kit (SDK).
User pools provide:
- Sign-up and sign-in services.
- A built-in, customizable web user interface (UI) to sign in users.
- Social sign-in with Facebook, Google, Amazon, or Apple, as well as sign-in with SAML identity providers from your user pool.
- User directory management and user profiles.
- Security features such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), checks for compromised credentials, account takeover protection, and phone and email verification.
- Customized workflows and user migration through AWS Lambda triggers.
The mobile device integrates with authentication and services hosted on Amazon API Gateway, enabled with Amazon Cognito authorizer-enabled for gateway APIs to authenticate incoming requests, along with isolation of doctor and patient APIs.
The services hosted integrate with Amazon Lex services that host the voice conversational interface layer. This enables the bot required to interact and responds to the queries from doctor and patients utilizing Amazon Lex’s Intent capabilities, which represents an action the user wants to perform.
Examples of this are: a MakeAppointment Intents is created in Amazon Lex with respective slots fulfillment via Lambda bookAppoinment added.
Please refer to the code snippet below showing how a “delegate” function defines the appointment data, sends to Amazon Simple Queue Service (SQS), saves to Amazon DynamoDB, and confirms it via Amazon Pinpoint:
def delegate(session_attributes,intent_request):# call db to save appointment details.AppointmentType = intent_request['currentIntent']['slots']['AppointmentType']Time = intent_request['currentIntent']['slots']['Time']Date = intent_request['currentIntent']['slots']['Date']mobileNumber=session_attributes['Mobile'] # ddb_encrypt_data can be called to encrypt data before updating DBmobileNumber= ddb_encrypt_data(mobileNumber) patientData = {'id': mobileNumber,'AppointmentType':AppointmentType,'Time':Time, 'Date':Date} ddb_insert_data("scheduled_appointment", patientData) message_txt = 'Your appointment is booked on ' + Date + ' at' + Time #send message to SQS queue to send sms and update dynamodb tablesend_data_to_db_SQSQueue("scheduled_appointment",patientData)send_sms_to_SQSQueue(mobileNumber, message_txt ) # Send SMS directly via Pinpointmessages_txt = [message_txt]pp_send_sms(mobileNumber, messages_txt) session_attributes = intent_request['sessionAttributes'] return { 'sessionAttributes': session_attributes, 'dialogAction': { 'type': 'Close', 'fulfillmentState':'Fulfilled', 'message':{ 'contentType': 'PlainText', 'content': 'Your Appointment is Booked.' } }}Once the patient has confirmed with date and time slot for booking the appointment, SQS queues the request to define a decoupled architecture, and the message is picked up by provisioning function hosted on Lambda.
The Lambda function enables storing appointment information securely with encryption keys hosted on AWS Key Management Service (AWS KMS) and into Amazon DynamoDB.
Once an entry is made into DynamoDB, an SMS and push notification is sent to the appropriate end user receivers. The implementation is done with DynamoDB Streams enabled and a Lambda custom trigger that integrates with Amazon Pinpoint. This provides features to send push notifications, emails, text messages, and voice messages to users.
Once the entries are available in the database and notifications received, doctors can review appointments and patient details using the doctor service layer voice bot. Similar to patient voice bot, Amazon Lex provides the required Intents.
An example of this is a GetAppointments Intent to fetch the appointments.
A GetPatientDetails Intent is then created to fetch a particular patient’s details and with respective slots. Fulfilment is achieved via the GetAppointments service/function hosted on Lambda.
Similar intents can be created for broader use cases based on end user requirements.
Please refer to the code snippet below showing how a “delegate_patient_details” function fetches the patient’s details and appointment data via Amazon Lex:
def delegate_patient_details(session_attributes,intent_request): # call db to get patient details. name = intent_request['currentIntent']['slots']['name'] patientID = intent_request['currentIntent']['slots']['patientID'] patientInfo=ddb_get_patient_data("patient_list",name,patientID) patientInformation=json.dumps(patientInfo) session_attributes = intent_request['sessionAttributes'] return { 'sessionAttributes': session_attributes, 'dialogAction': { 'type': 'Close', 'fulfillmentState':'Fulfilled','message':{
'contentType': 'PlainText', 'content': patientInformation }}
} def delegate_appointment_list(session_attributes,intent_request): # call db to get appointment details. date = intent_request['currentIntent']['slots']['date'] appointment_list=ddb_get_data("scheduled_appointment", date) appointmentInformation=json.dumps(appointment_list)session_attributes = intent_request['sessionAttributes']
return {
'sessionAttributes': session_attributes, 'dialogAction': { 'type': 'Close', 'fulfillmentState':'Fulfilled', 'message':{ 'contentType': 'PlainText', 'content': appointmentInformation } } }After a doctor fetches the patient’s details, they can do the initial triage and prescribe remedies via voice, based on the symptoms and other information provided by the patient during the initial integration with the system.
The doctor’s voice recording is stored in Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3), and then converted to unstructured text via Amazon Transcribe Medical. This is a is a HIPAA-compliant service providing an automatic speech recognition (ASR) service that enabled us to add medical speech-to-text capabilities to the service.
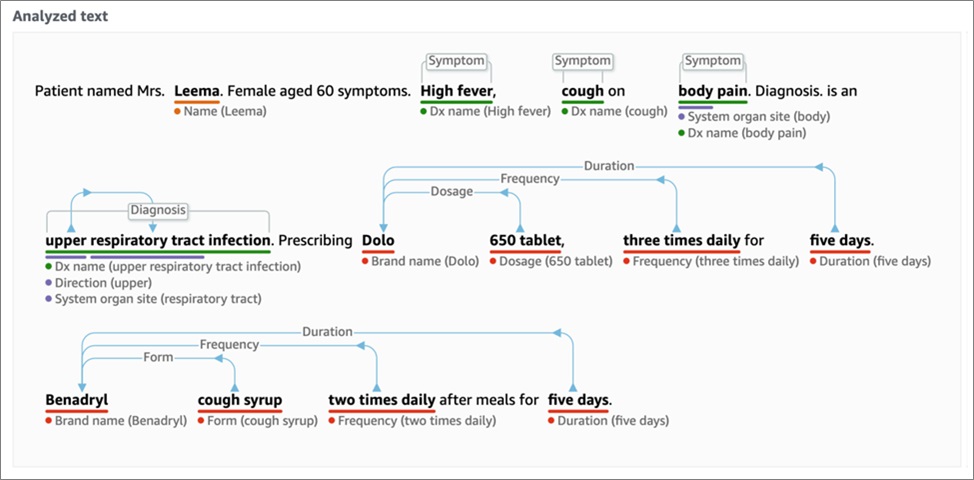
Once the unstructured text is created, the text is used by Amazon Comprehend Medical, a natural language processing (NLP) service that uses machine learning to extract relevant medical information from unstructured text.
Using Amazon Comprehend Medical enables us to quickly and accurately gather information, such as medical condition, medication, dosage, strength, and frequency from a variety of sources like doctors’ notes, clinical trial reports, and patient health records.
Amazon Comprehend Medical can also link the detected information to medical ontologies such as ICD-10-CM or RxNorm, so it can be used by downstream healthcare applications.
The model can segregate entities like symptoms, diagnosis, dosage, frequency, and duration, which can be sent via API to the mobile application display so doctors can validate and prescribe medication to their patient. The model can be further trained as required.
Below are the key highlights of the architecture design:
- 100 percent serverless solution.
- OAuth 2.0 secured REST API calls for secure voice capture device and API integration.
- Microservices implementation that scales and provisions to load, ensuring cost is directly associated with usage trends.
- Quick time-to-market and easy provision.
- Standard message queues configured to channelize SMS and push notifications and database updates asynchronously.
- Protecting data using encryption in transit and at rest.
Capgemini’s solution provides benefits to both patients and doctors. Via voice prompts, the modular nature of the solution enables doctors to:
- Generate prescriptions and view bookings (past, new, upcoming).
- Generate prescriptions.
- Act as an assistant that can generate structured medical prescription and document from a voice dictation.
- Be used as a smart assistant, without human assistance.
- Medical practitioners are freed with gloves and masks to diagnosis patient reports.
From a patient’s perspective, the solution enables via voice prompts:
- Quick and easy voice-based appointment booking system.
- Medical prescriptions, monitoring information, history of appointments, and other diagnoses documents delivered to the mobile app.
- SMS and push notifications for appointment booking.
Ensuring security
Implementing security features for these APIs is critical, as the details held in the solution are personal identifier implementation.
The concept solution implements the following feature out of the box:
- OAuth 2.0 secured REST API calls for secure voice capture device and API integration.
- Personal identifiable information (PII) and medical history secured with GDPR and HIPAA-compliant architecture.
- Access limited by username and password authentication with Amazon Cognito.
- Protect data by encryption at rest and in transit with AWS KMS.
- Encrypted message notification.
- Designed on HIPAA-compliant AWS services with emphasis on cost effectiveness.
- Hosted within secure Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC).
Designing for reliability
Designing applications for reliability helps withstand component failures for critical components. As such, the following are some of the main design aspects used to design system components for fault tolerance and auto recoverability:
- AWS-native and managed services implementation.
- True microservices implementation that scales and provisions to load as per usage.
- Serverless computing hides server usage from the developers and runs code on-demand automatically scaled.
- Amazon DynamoDB supports great reliability and scalability while executing ACID transactions.
- SQS stores all the messages in a highly available AWS region with multiple redundant AWS Availability Zones, so that no single computer, network, or failure can make messages inaccessible.
- System or component issues can be easily integrated through SIAM.
Lessons learned
The implementation came with its own lessons and challenges due to the innovative nature of the solution.
To protect patient and doctor PII:
- Use AWS KMS and access policies for data at rest encryption, and for data saved in Amazon DynamoDB and Amazon S3.
- Consider using customer-owned keys.
- Use Amazon Cognito and Amazon API Gateway for handhelp device’s security and compliance while connecting to AWS services.
To manage millions of operations at a time, we selected to go with AWS managed services for scalability and performance optimizations. This also ensured the overall cost and runtime of the environments required can be minimized. Operational efficiencies in terms of patch management and upgrades were also addressed due to the managed services.
Finally, decoupling provided the best architecture for isolating and triaging issues during development. This, in turn, increased the build-test turn around and increased the number of updates possible.
Conclusion
Pandemics can bring forward a lot of technology and productivity challenges; even more so for doctors, practitioners, and patients, who require a working environment that is risk-free and achieves maximum productivity.
In this post, we have shown how Capgemini can hep simplify pandemic management for doctors with AWS machine learning services.
Capgemini recognizes that provisioning, designing, and implementing a solution on the cloud is different to how it’s done on-premises. As such, Capgemini works with AWS service features that enable customers to do prototypes as part of design phase. This helps customers solve productivity, business, and operational challenges with solutions that comply to international security standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI.
Visit us to learn more about AWS and Capgemini, and get in touch with one of our experts.
Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning
Read More from This Article: How Capgemini Simplifies Pandemic Management with AWS Machine Learning Services
Source: News