The traditional supply chain has a lot of inefficiencies and bottlenecks that can lead to losses and pilferage.
There are losses because of logistical inefficiencies, or because perishable goods or drugs may not be transported in the required time period. There can also be losses due to environmental excursions, as many drugs are sensitive to shock, temperature or humidity, and exposure to the wrong conditions can deem them ineffective.
In this post, we will share an architectural reference from Capgemini for an Amazon Web Services (AWS) solution called Trusted Logistics that can help solve these problems in the pharmaceutical industry.
Capgemini’s solution addresses three main problem areas:
- Monitoring and maintaining specific temperatures, humidity, and vehicle locations, along with a real-time dashboard, alerts, and logistic checks while in transit. This must happen from the start of drug manufacturing until the units reach a retail medical store, for example.
- Controlling commonplace drug counterfeiting by keeping immutable ledger entries of a drug’s entire journey, while also tracking that someone is not able to change the drug by opening the container.
- Tracking, tracing, and recall of drugs post-manufacturing, from the manufacturer to the pharmacy it’s being shipped to.
Capgemini is an AWS Premier Consulting Partner and Managed Service Provider (MSP). With a multicultural team of 220,000 people in 40+ countries, Capgemini has more than 12,000 AWS accreditations and over 2,700 active AWS Certifications.
Solution overview
With Trusted Logistics, Capgemini’s industry expertise and AWS services come together to enable organizations to leverage the Internet of Things (IoT), blockchain, and serverless to gain real-time visibility into their shipments while preventing drug counterfeiting.
The solution architecture uses AWS IoT Core to gain real-time visibility into shipments, and Amazon Managed Blockchain for all transactional data to ensure a high degree of security and transparency and reduce the chances of fraud and counterfeit.
Trusted Logistics is built over a serverless stack, which reduced time to market, complexity, and ultimately the cost of running a reliable and scalable server.
The solution also provides a customized dashboard for each participant involved in the supply chain, such as legal, logistics providers, distributors, and pharmacies.
Furthermore, the solution provides insights on optimized routes based on intel gathered from unfavorable events and alerts combined with QR code tracking capabilities to reduce the manual operation overhead.
The goal of Trusted Logistics is to make sure the supply chain itself has the ability to track and trace from manufacturing to end customers.
How it works
Capgemini’s solution provides an interface for all stakeholders in the supply chain landscape and encompasses the following:
- Creating a trip and assigning details to the trip
- Tracking dashboard
- Alerts and notifications
- Shipment status
- Incident insights
- Record receipt of goods
- Record consignment dispatch
- Track transaction
- SAP IDOC integration
- QR code based identification
First, data ingestion will happen from the manufacturer’s SAP system, where drug details for delivery are fed to Trusted Logistics. The transaction is then recorded in a decentralized ledger.
The manufacturer hands over the consignment to the logistics provider, and a change of ownership is added to the solution’s audit system.
Trip details are fetched from the logistics external system. Data is received from sensor-fitted containers and packages leveraging AWS IoT services to enable live monitoring.
If the minimum value of a shipment’s health parameters are breached, the solution sends an alert by using Amazon Simple Notification Service (SNS) and makes an audit entry into AWS Managed Blockchain for anomalies.
The solution provides an intuitive map view for logistics operators so they can track shipments, and provides real-time views into shipment health.
When the consignment reaches the distributor, they perform a verification. After verifying the package, an acknowledgement is issued to add purchase order details for confirmation, and an audit event is added to the system.
When a pharmacy receives and acknowledges these drugs, they can provide the same information to a consumer when shown the relevant prescription.
The consumer can scan the QR code with a mobile app, on which they’ll be able to view details regarding the origin, production, and transit of the drug. This helps validate the authenticity of the drug and traceability to the origin. Once the drug has been sold to the consumer, an audit event is added to the system.
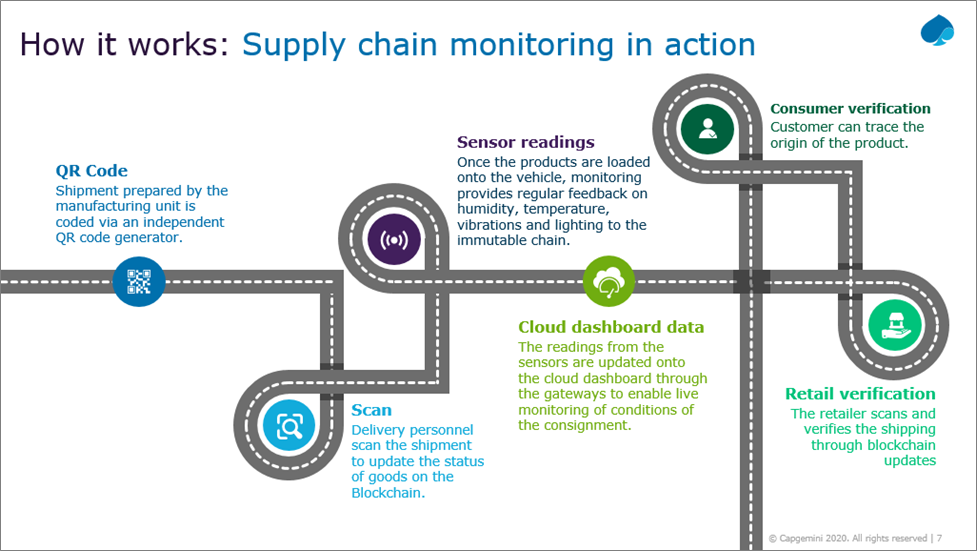
The diagram in Figure 1 below represents a simple supply chain, which is like moving the goods from a factory to the retailer, essentially the tracking of goods using a QR code.
The system generates the QR code for the tracking of goods. Each consignment that gets shipped from the manufacturer unit has a unique QR code that’s scanned at each and every juncture.
The sensor readings are transmitted while the products are in transit, and whenever there’s a breach of sensor parameter it gets recorded to Amazon Managed Blockchain for better traceability using AWS IoT devices comprising condition monitoring sensors like temperature, humidity, vibration.
These devices will be used to track entire containers or pallets or individual item boxes. The device data is transmitted to cloud applications using low bandwidth network connections, such as MQTT protocol to AWS IoT Core in real-time or at present time interval.
AWS IoT Core securely ingests sensor data and forwards it to AWS IoT Analytics, where massaging, enriching of sensor data with device-specific metadata happens, before storing it to time series data store.
Since the products are tracked using a unique ID, if anything else gets inside the ethical supply chain, the system will catch it.
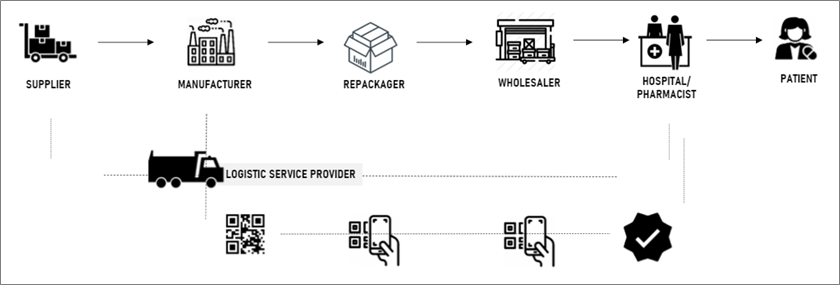
The following diagram in Figure 2 represents the process view of drug flow. This starts with a Serialization ID at the time of manufacturing, which can be traced through QR codes and takes care of the product safety throughout the supply chain.
To ensure transactional safety, this blockchain system is supported with IoT technology which sends out regular signals to the trade partners. Blockchain records each time a drug changes hands, assisting companies in detecting tainted products before they reach consumer.
Blockchain provides a secure approach for all participants in the supply chain to interact and ensure integrity of all the supply chain transaction.
Tackling and preventing counterfeiting
Using state-of-the-art technology combining IoT and blockchain, here are a few examples of how Trusted Logistics prevents the entry and sale of counterfeit drugs into the market:
- If someone tries to create a QR code that looks genuine but is not generated by Capgemini’s solution, a drug scan would render no information and imply a counterfeited drug.
- If someone tries to swap the genuine product with the falsified medicine, Trusted Logistics can—with the help of an unscheduled door opening event under the IoT solution—inspect the whole batch and replace it, if required.
- If the QR code is duplicated and the drug is simultaneously available in two places, with the help of audit information that’s been added each time and at every juncture, the system can detect the anomalies instantly and the consumer will be notified.
- If someone tries to use and sell a used vial of drugs by adding falsified medicines, a drug scan would render information that drugs have been sold, with bill number and date.
- In case a recall has happened for a particular batch of drugs and the drugs are still being sold by the pharmacy, consumers will be notified about the recall and advised not to purchase it after scanning. This is facilitated by the broadcast details fed during the audit entry to the system.
Solution architecture
Trusted Logistics will be implemented as a consortium blockchain to govern the platform. It’s a permissioned platform and has multiple participants, as any organization in a supply chain can make decisions on the platform.
No one can get away with illegal activities. All participants on the platform will keep everyone in check. It uses a consensus mechanism to reach an agreement.
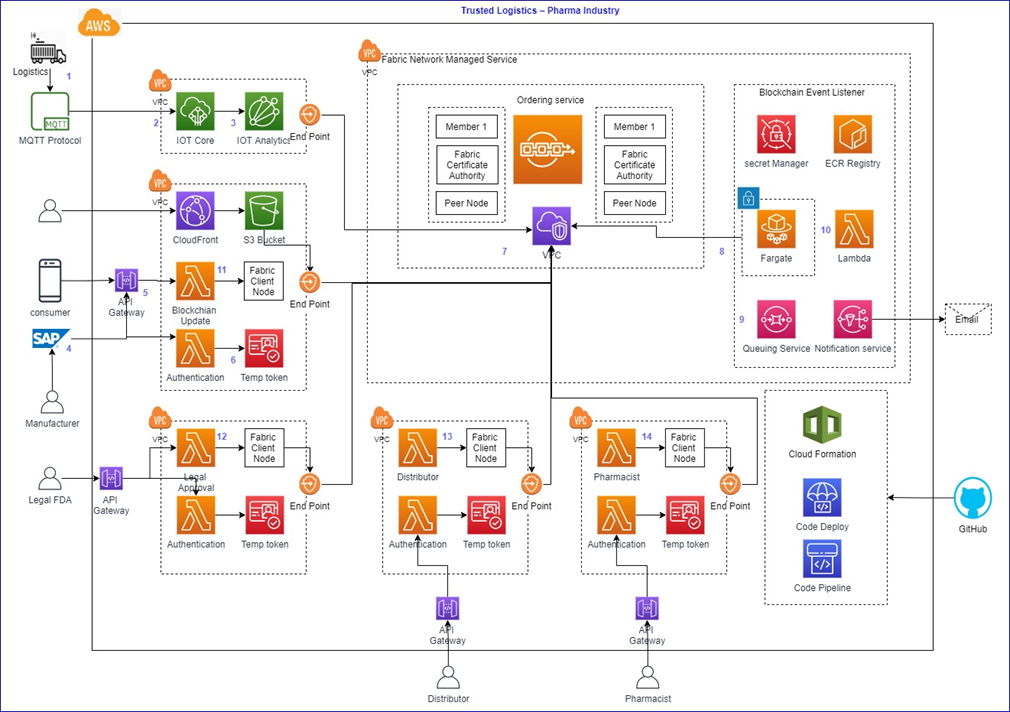
The architectural diagram below represents the process view of data flow from an organization’s SAP system, and the sensor data with sensor fitted in containers and packages.
Let’s take a detailed look and the solution architecture:
- While in transit, a vehicle’s sensor data moves to AWS IoT Core with help of M2M network and MQTT protocol. MQTT protocol is a lightweight, efficient protocol and, by default, is encrypted when talking to AWS IoT Core.
- AWS IoT Core enables connected devices to securely interact with cloud applications and other devices. It consists of Message Broker, Registry, Device Shadow, Rule Engine, and Security. Message Broker provides the publish/subscribe interface where you listen into the topics and subscribe to that topic.
Registry is the database of all IoT devices. Device Shadow is the location for persistence information; as the MQTT is a publish/subscribe protocol and there’s not really a place in these for persistence.
Rule Engine is a place where we can automate a lot of integration to other AWS services by listening to a particular topic. It’s like having a SQL-language interpreter who tells you what’s being written onto a particular topic, and then delivers it to other AWS services like Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3), Amazon Kinesis, and Amazon DynamoDB. - The sensor data is being fed from AWS IoT Core to AWS IoT Analytics, which operationalizes sophisticated analytics on massive volumes of unstructured IoT data. AWS IoT Analytics filters alerts and anomalies, transforms, and enriches IoT data before storing it in a time-series data store for analysis, and before posting into Amazon Managed Blockchain.
- The solution has been integrated with SAP, which sends master and transactional data. SAP sends IDOC data.
- The SAP IDOC integrates with authentication and services hosted on Amazon API Gateway, enabled with Amazon Cognito authorizer for gateway APIs to authenticate incoming requests from the SAP system.
- Amazon Cognito services are used as part of the authentication, with user pools created separately for all organization in the network.
- Amazon Managed Blockchain is a fully managed service for creating and managing blockchain networks and network resources using open-source frameworks. Blockchain allows you to build applications where multiple parties can securely and transparently run transactions and share data without the need for a trusted, central authority.
The Trusted Logistics solution incorporates Smart Contract, which is being triggered based on the event created in the blockchain network. - When an event is created, the listener that’s deployed on AWS Fargate allocates the right amount of compute. This eliminates the need to choose instances and scale cluster capacity, and the solution publishes this event to Amazon Simple Queue Service (SQS).
- Using SNS and SQS together, messages can be delivered to applications that require immediate notification of an event, and also persisted in an SQS queue for other applications to process at a later time.
- An AWS Lambda function processes messages from this queue and sends notifications to the concerned parties through SNS.
- The services hosted integrate with Lambda to send readings to Amazon Managed Blockchain with SAP supply chain events, like the change of ownership and state change of any product. This enables quick auditing and identification of source of product batches and their quality within a short period of time, which could result in efficient product traceability.
- The services hosted integrate with Lambda to update the approval status in Amazon Managed Blockchain by Legal FDA.
- The hosted services integrate with Lambda to update the status of acknowledged and dispatch consignment and the environmental condition of the goods in the warehouse into an Amazon Managed Blockchain by a distributor.
- The hosted services integrate with Lambda to update the status of the goods received and sold into the Amazon Managed Blockchain by a pharmacist.
Each participant will have the customized dashboard where data is being showed based on their role:
- For legal, the web user interface (UI) shows the pending approval records, and Lambda will update the approval status in Amazon Managed Blockchain.
- For logistics, the dashboard will have a bird’s eye view of trips, incidents, and alerts.
- A trip operator can view scheduled and ongoing trips, and can take proactive action on alerts received.
- For distributors, the web UI tracks the progress of the consignment and includes acknowledgement and dispatch.
- The pharmacy will have a drug sales option and QR code screen for scanned drugs.
Code snippets
In the Trusted Logistics solution, Amazon S3 stores all IDOC data received from the SAP system. The following code snippets read S3 events which contains the IDOC file in .xml format, validates the IDOC file and processes, and transforms and maps the IDOC file into respective tables.
This code will be invoked when any IDOC is created in SAP and pushed it to Trusted Logistics:
module.exports = async function data(event) { console.log("Reading options from event:n",util.inspect(event, { depth: 5 }));const srcBucket = event.Records[0].s3.bucket.name;console.log("Bucket Name ", srcBucket);const srcKey = decodeURIComponent(event.Records[0].s3.object.key.replace(/+/g, " "));console.log("Object Key ", srcKey);const s3Params = { Bucket: srcBucket, Key: srcKey, }; try { var streamData = await s3.getObject(s3Params).promise(); console.log("Stream data : ", streamData.Body.toString("utf-8")); var IdocBody = streamData.Body.toString("utf-8"); var IdocJson =await convert.xml2json(IdocBody, { compact: true, spaces: 4 }); var IdocJsJsonObject = await JSON.parse(IdocJson); }if (validate(IdocJsJsonObject)) { var mapIdocDataToFIelds = mapping.mapDeliveryFields; var transformedResult = transform(IdocJsJsonObject, mapIdocDataToFIelds); const Insert_Delivery_Query_Stmt = query.DeliveryInfo; const deliveryDataValues = querydata.values(transformedResult); var response = await dbcall(Insert_Delivery_Query_Stmt, deliveryDataValues); }Features and benefits
The Trusted Logistics solution is built on a serverless stack and uses AWS native and managed services. It ensures security, as access is limited by username and password authentication with Amazon Cognito.
The objects in Amazon S3 have encryption keys, and all of the API calls are accessed using Amazon API Gateway, which supports SSL/TLS along with AWS WAF which protects APIs from SQL injection and cross-site scripting attacks.
All of the transactions in the hyperledger fabric are secured by certificates issued by certificate authority (CA).
Lessons learned
To manage millions of operations at a time with Trusted Logistics, Capgemini chose to go with AWS managed services for scalability and performance optimizations. This also ensured the overall cost and runtime of the environments required can be minimized.
Operational efficiencies in terms of patch management and upgrades were also addressed due to the managed services.
Serverless computing hides server usage from the developers and runs code on-demand automatically scaled.
Conclusion
Trusted Logistics can be applied to multiple sectors like manufacturing, retail, consumer product, logistics, life sciences, and more.
Leveraging Serialization IDs and IoT monitoring enables all supply chain participants to interact with one another to ensure the integrity of transactions. A decentralized ledger is accessible to all participants and transaction records become immutable once entered.
Visit us to learn more about AWS and Capgemini, and get in touch with one of our experts.
Internet of Things
Read More from This Article: Capgemini’s Trusted Logistics and Drug Counterfeit Solution for the Pharma Industry
Source: News