Artificial intelligence (AI)-enabled systems are driving a new era of business transformation, revolutionizing industries through prescriptive analytics, personalized customer experiences and process automation. From manufacturing to healthcare and finance to defense, AI enhances efficiency, decision-making and operational agility, providing organizations a competitive edge in an increasingly data-driven world. Its processing of vast datasets enables supply chain precision, life-saving diagnostics and hyper-personalized consumer interactions, fostering scalability and innovation.
However, as AI adoption accelerates, organizations face rising threats from adversarial attacks, data poisoning, algorithmic bias and regulatory uncertainties. Without robust security and governance frameworks, unsecured AI systems can erode stakeholder trust, disrupt operations and expose businesses to compliance and reputational risks.
Senior executives are challenged with securing AI, aligning initiatives with governance frameworks and fortifying business resilience. Organizations can unlock AI’s full potential by proactively addressing security, ethics and operational challenges while ensuring transparency, reliability and long-term sustainability.
The risks of unsecured AI
Unlike traditional IT systems, AI is uniquely susceptible to novel attack vectors such as:
- Adversarial attacks. Subtle input data manipulations can cause AI systems to make incorrect decisions, jeopardizing their reliability.
- Data poisoning. Compromised datasets used in training AI models can degrade system accuracy.
- Generative AI risks. Issues like hallucinations and malicious prompt injections threaten enterprises reliant on AI-generated content.
Ethics and governance in AI
AI also challenges organizations to address algorithmic bias, transparency and accountability issues. Regulatory frameworks like the EU AI Act and NIST AI Risk Management Framework are shaping expectations around responsible AI deployment.
Balancing security, ethics and strategic investments
Securing AI systems requires a balanced approach that integrates technical rigor with strategic foresight:
- Invest in AI-specific security. Tools like adversarial training and robust data validation can prevent common attack vectors.
- Adopt ethical AI frameworks. Promoting fairness and inclusivity in AI systems builds trust and mitigates reputational risks.
- Future-proof AI systems. Continuous monitoring, adaptive governance and upskilling talent ensure resilience against evolving challenges.
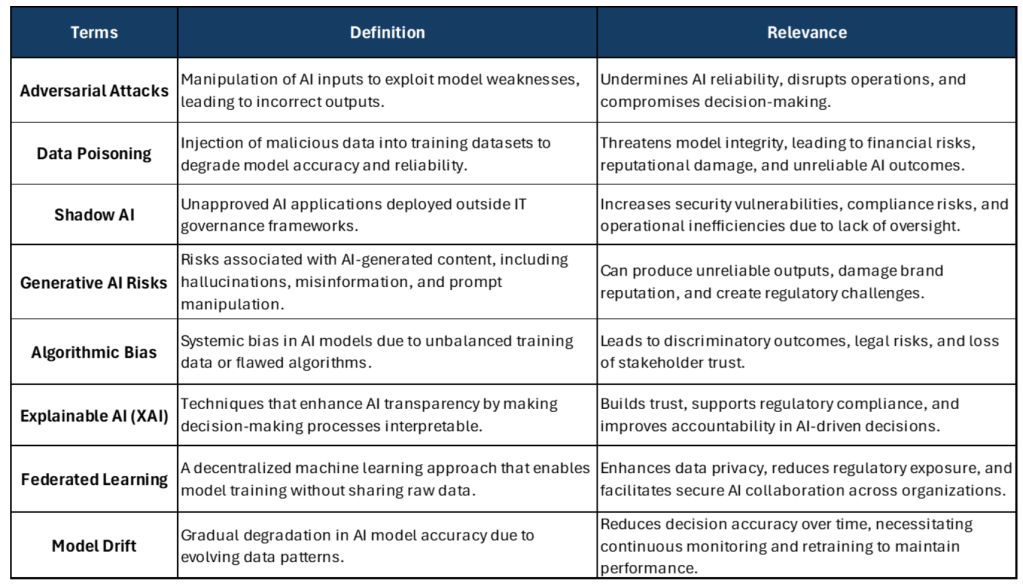
Key AI security concepts
Review critical AI security terms, their definitions, relevance and interrelationships around AI governance and resilience. Understanding these foundational concepts helps organizations build secure, ethical and scalable AI that aligns with business goals and regulatory requirements.
Vipin Jain
The following provides a quick overview of interrelationships among these terms and an overall ecosystem impact:
- Dependencies. Adversarial attacks, data poisoning and generative AI risks exploit data governance and security gaps.
- Complementary solutions. Explainable AI and federated learning address transparency and privacy concerns.
- Audits. Bias audits and adversarial training improve reliability.
- Holistic approach. Establishes the foundation for secure, ethical and scalable AI systems, enabling organizations to mitigate risks.
Addressing these key areas can help organizations create resilient AI frameworks that balance security, ethics and efficiency.
Drivers, challenges and strategic importance
AI has become a fundamental driver of business transformation, allowing organizations to enhance efficiency, refine decision-making and create personalized customer experiences. However, AI adoption also presents complex challenges, including security vulnerabilities, ethical concerns and regulatory compliance. Understanding these drivers, challenges and the strategic importance of AI security is essential for organizations aiming to maximize AI’s potential while mitigating risks.
Drivers
Organizations across industries are using AI to drive business innovation and operational efficiency. Several key factors contribute to the widespread adoption of AI:
- Business transformation. AI improves workflows, enhances decision-making and delivers hyper-personalized customer experience.
- Healthcare. AI-driven diagnostics improve accuracy and early disease detection.
- Finance. AI-powered fraud detection prevents financial losses in real-time.
- Retail. Recommendation engines personalize shopping experiences, boosting sales.
- Regulatory compliance. Governments are mandating stricter AI governance to ensure transparency and fairness.
- EU AI Act. Requires explainability and imposes penalties for non-compliance.
- US NIST AI Framework. Defines security best practices for AI deployment.
- Stakeholder trust. Ethical AI adoption fosters customer, employee and partner trust.
- Transparent AI models reassure stakeholders about fairness in decision-making.
- Inclusive AI reduces bias, promoting fair access to services.
Challenges
Despite its benefits, AI adoption introduces a range of challenges that require initiative-taking risk management:
- Cybersecurity threats. AI systems are uniquely vulnerable to advanced cyberattacks.
- Adversarial attacks. Attackers manipulate AI inputs to produce incorrect outputs.
- Model theft. AI intellectual property can be stolen and exploited.
- Data governance gaps. Poor data management can lead to compromised AI integrity.
- Data poisoning. Corrupt training data leads to inaccurate AI predictions.
- Lack of data lineage. Inconsistent data tracking hinders compliance.
- Algorithmic bias. Biased training datasets can perpetuate systemic discrimination.
- Operational inefficiencies. AI models still require ongoing maintenance to be effective.
- Model drift. AI models lose accuracy over time due to changing data patterns.
- Generative AI hallucinations. AI-generated outputs can become unreliable.
- Shadow AI. Unauthorized AI deployments outside IT governance create security and compliance risks.
Strategic importance
To maximize AI’s potential while mitigating risks, organizations must integrate AI security and governance into their long-term strategies:
- Protecting operational integrity. Proactively addressing AI vulnerabilities ensures uninterrupted business operations and safeguards performance.
- Ensuring ethical practices. Adopting fairness, accountability and transparency in AI systems builds stakeholder confidence and regulatory alignment.
- Fostering innovation. Effectively managing AI risks allows organizations to use AI as a competitive advantage while driving sustainable growth.
By addressing these drivers and challenges, organizations can strategically position themselves to unlock AI’s full potential, ensure long-term resilience and foster a secure and ethical AI ecosystem.
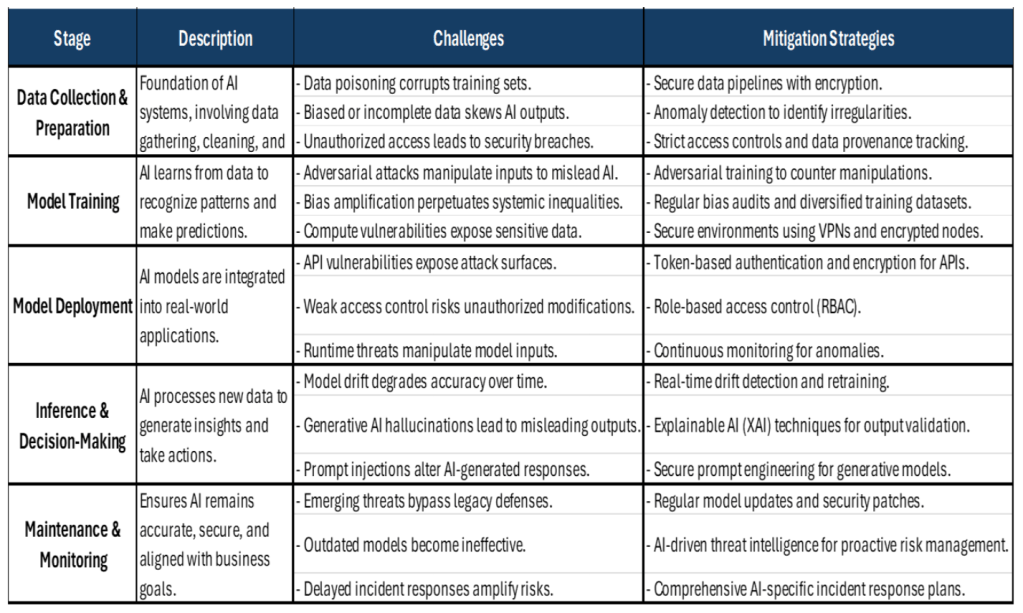
Fortifying AI frontiers across the lifecycle
Securing AI requires a lifecycle approach that addresses risks from data collection to deployment and ongoing monitoring. Without robust security, governance and risk mitigation, AI systems can be exploited through adversarial attacks, data manipulation and ethical breaches. To ensure secure, transparent and compliant AI, organizations should adopt three foundational strategies:
- Governance. Implement AI-specific risk frameworks such as the NIST AI Risk Management Framework and enhance transparency with Explainable AI (XAI) for regulatory compliance.
- Continuous monitoring. Deploy real-time threat detection and model drift monitoring to proactively manage vulnerabilities and prevent AI degradation.
- Collaborative ecosystems. Align IT, compliance, cybersecurity and business teams to enforce AI governance and ensure security and ethical integrity.
By securing AI at every stage of its lifecycle, organizations can fortify AI innovation while mitigating security risks, supporting compliance and sustaining business trust. The following table provides a quick overview of artificial intelligence lifecycle stages:
Vipin Jain
4 critical AI security strategies
1. Adversarial training: Strengthening AI against manipulations
Adversarial training fortifies AI models by exposing them to simulated attacks, making them more resilient against data manipulation, cyber threats and fraud. A global logistics firm implemented adversarial training in its route optimization AI, reducing disruptions from data tampering by 25%. This method enhances AI’s ability to detect malicious inputs and prevent exploitation in fraud detection, image recognition and autonomous decision-making.
2. Explainable AI (XAI): Enhancing transparency and trust
XAI clarifies AI-driven decision-making, helping businesses build trust, reduce bias and meet regulatory requirements. A healthcare provider leveraged XAI tools to make its AI-driven diagnostic recommendations more transparent, improving physician confidence by 30%. In regulated industries like finance, healthcare and insurance, XAI supports auditability, compliance and ethical AI.
3. Secure data pipelines: Protecting AI from data tampering
Ensuring data integrity is critical for AI reliability. Secure data pipelines safeguard AI models from data poisoning, unauthorized access and compliance violations through encryption, access controls and anomaly detection. Businesses can maintain accuracy and regulatory compliance by ensuring that only confirmed, unbiased and tamper-proof data is fed into AI models.
4. Real-time monitoring: Detecting and mitigating AI risks
AI systems require continuous oversight to detect anomalies, performance drift and emerging cyber threats. A financial institution implemented real-time AI monitoring for its credit scoring system, reducing fraud-related losses by 20% and ensuring ongoing model accuracy. Continuous monitoring solutions help find vulnerabilities 85% faster, ensuring that AI stays stable, secure and aligned with business aims.
The path forward
Organizations must integrate adversarial defense, explainability, secure data management and real-time risk monitoring into their AI strategies to fortify AI security. These measures safeguard AI integrity, enhance compliance and build stakeholder trust. Proactively addressing AI risks through strategic governance and security frameworks allows businesses to drive innovation while ensuring ethical responsibility and long-term sustainability. By adopting these strategies, organizations can strengthen AI security, support transparency and uphold compliance while refining efficiency and reinforcing stakeholder confidence.
The competitive AI landscape
The rapid adoption of AI has created a thriving ecosystem of vendors offering innovative solutions for securing AI systems, managing governance and ensuring ethical compliance. Understanding these players’ strengths and limitations is essential for informed decision-making in technology investments.
Microsoft Azure AI
Microsoft Azure AI provides a robust AI ecosystem that integrates Microsoft’s cloud and enterprise solutions. Prebuilt security frameworks like Azure AI Defender and Azure Sentinel are ideal for regulated industries such as finance and healthcare. While scalable and compliant, its prohibitive cost and complexity can hinder smaller organizations. Gartner ranks Azure AI among the top three enterprise AI security solutions.
Google Cloud AI
Google Cloud AI specializes in AI governance, security and explainability (XAI), making it an excellent choice for enterprises requiring transparent and compliant AI. Its XAI tools support regulatory adherence in healthcare and finance, though limited customization and premium pricing may be drawbacks.
AWS AI
Amazon Web Services (AWS) AI offers comprehensive AI security and scalability, with AWS Sage Maker widely used for secure model training and deployment. Its global infrastructure supports large-scale enterprises, but excessive costs and third-party integration challenges may hinder smaller firms.
Darktrace
Darktrace is a leader in AI-powered cybersecurity, offering real-time anomaly detection and autonomous threat mitigation. Its self-learning AI models adapt to evolving threats, making it essential for enterprises requiring continuous security monitoring. However, inflated costs and complex deployment may limit adoption for smaller businesses.
These vendors shape AI security’s future, offering specialized solutions in threat detection, explainability and data integrity. As AI adoption accelerates, their technologies will be key to ensuring secure, compliant and ethical AI deployment.
Market trends and strategic implications
The AI security market is experiencing rapid growth and is projected to expand at a 28% CAGR, reaching $50 billion by 2030. North America currently leads with a 45% market share, followed by Europe and the Asia-Pacific region, reflecting a global emphasis on AI security. This growth is driven by increasing regulatory compliance mandates, the evolving sophistication of AI-related threats and a rising focus on ethical AI practices. Organizations across industries recognize the need to implement robust security frameworks that address adversarial attacks, data governance challenges and algorithmic bias to ensure AI systems stay secure and trustworthy.
Future focus
AI security is evolving rapidly, with innovative technologies and frameworks shaping the future landscape. Organizations must expect emerging trends to still be competitive and resilient.
- AI-driven threat intelligence transforms cybersecurity by enabling real-time detection and mitigation of sophisticated threats. AI-powered systems analyze vast data streams to find anomalies, predict cyberattacks and neutralize risks before they escalate. Darktrace employs AI for anomaly detection, reducing breach risks by 40% and reinforcing AI’s role in initiative-taking security management.
- Regulatory frameworks for AI governance are becoming increasingly stringent. The EU AI Act mandates transparency and accountability, with substantial penalties for non-compliance. Organizations that invest early in compliance frameworks gain a competitive advantage, regulatory readiness and stronger stakeholder trust, ensuring AI deployments stay ethical, secure and aligned with legal requirements.
Conclusion
AI systems are driving unparalleled innovation and operational efficiency across industries. However, securing these systems against technical, ethical and regulatory challenges requires a holistic, forward-looking approach. Organizations can adopt the right strategies to ensure their AI frontiers, foster stakeholder trust and sustain growth in an increasingly AI-powered world.
Vipin Jain, founder and chief architect of Transformation Enablers Inc., brings over 30 years of experience crafting execution-ready IT strategies and transformation roadmaps aligned with business goals while leveraging emerging technologies like AI. He has held executive roles at AIG, Merrill Lynch and Citicorp, where he led business and IT portfolio transformations. Vipin also led consulting practices at Accenture, Microsoft and HPE, advising Fortune 100 firms and U.S. federal agencies. He is currently a senior advisor at WVE.
This article was made possible by our partnership with the IASA Chief Architect Forum. The CAF’s purpose is to test, challenge and support the art and science of Business Technology Architecture and its evolution over time as well as grow the influence and leadership of chief architects both inside and outside the profession. The CAF is a leadership community of the IASA, the leading non-profit professional association for business technology architects.
Read More from This Article: AI’s Achilles heel: Securing the next revolution
Source: News

